Neda Libre Services Integration Platform (Neda-LSIP)
Neda Libre Services Integration Platform (Neda-LSIP)
Design and Implementation Notes
Draft Document – Reflects Work in Progress
Document Nu: PLPC-110501
Mohsen Banan
http://mohsen.banan.1.byname.net/ContactMe
January 5, 2008
Contents
1 Open Services Management Tools
1.1 Server To Services Transformation
1.2 Open Services Management Tools
1.3 GOALS
1.4 Common Features
1.5 Obtaining LSIP
1.6 LSIP License
1.7 LSIP Overview
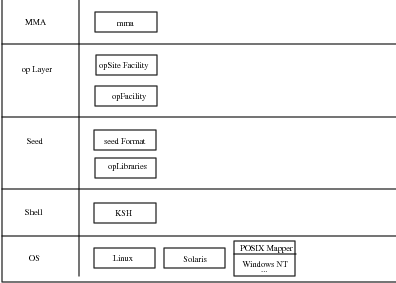
II Libraries and Seeds
1.8 Libre Platform Definitions
III Libre Platform Base
2 Open Platform Libraries
2.1 doLib
2.2 visLib
2.3 ocp-lib
2.4 ocp-general
2.5 ocp-lineNu
2.6 ocpLibUse
2.7 opRunEnvLib
2.8 opWrappersLib
2.9 itemsLib
2.9.1 Visibility Rules
2.9.1.1 items Visibility
2.9.1.2 runMode Visibility
2.9.1.3 Cluster Visibility
2.9.1.4 Binary Visibility
2.10 opDoAtAsLib
3 Seed Scripts
3.1 seedActions.sh
3.1.1 Description
3.1.2 Example
3.2 seedSubjectAction.sh
3.2.1 Description
3.2.2 Example
IV Base Platform and Site Abstraction
4 Site and Clusters Selection
4.1 opHosts
4.2 opSites
4.3 opClusters
4.4 opDomains
4.4.1 opSysIdentities
5 Conventions
5.1 Introduction
5.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Tools
5.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Tools
5.1.3 Hints – MMA Tools
5.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Tools
V Package and Distribution Facilities
6 Linux Distribution Abstractions
7 BinsPrep
8 Operating System Installation
8.1 opGenesis
VI Host and Site Administration
9 Disk Management Tools
9.1 Model and Terminology – Disk Management Tools
9.2 Files Overview – Disk Management Tools
9.3 Hints – Disk Management Tools
9.4 Pointer and References – Disk Management Tools
VII Disk and Storage Facilities
VIII System Foundation Facilities
9.5 MMA Daemon Tools
9.5.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Daemon Tools
9.5.2 Files Overview – MMA Daemon Tools
9.5.3 Hints – MMA Daemon Tools
9.5.4 Pointer and References – MMA Daemon Tools
IX Network Foundation Facilities
10 L2 Facilities
11 L3 Facilities
11.1 MMA Layer 3
11.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Layer 3
11.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Layer 3
11.1.3 Hints – MMA Layer 3
11.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Layer 3
12 UCSPI
12.1 MMA Ucspi
12.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Ucspi
12.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Ucspi
12.1.3 Hints – MMA Ucspi
12.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Ucspi
13 Misc
13.1 MMA FTP
13.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA FTP
13.1.2 Files Overview – MMA FTP
13.1.3 Hints – MMA FTP
13.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA FTP
13.2 MMA GNATS
13.2.1 Model and Terminology – MMA GNATS
13.2.2 Files Overview – MMA GNATS
13.2.3 Hints – MMA GNATS
13.2.4 Pointer and References – MMA GNATS
13.3 MMA Rsync
13.3.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Rsync
13.3.2 Files Overview – MMA Rsync
13.3.3 Hints – MMA Rsync
13.3.4 Pointer and References – MMA Rsync
13.4 MMA Ssh
13.4.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Ssh
13.4.2 Files Overview – MMA Ssh
13.4.3 Hints – MMA Ssh
13.4.4 Pointer and References – MMA Ssh
13.5 MMA Sudo
13.5.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Sudo
13.5.2 Files Overview – MMA Sudo
13.5.3 Hints – MMA Sudo
13.5.4 Pointer and References – MMA Sudo
13.6 MMA Tftp
13.6.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Tftp
13.6.2 Files Overview – MMA Tftp
13.6.3 Hints – MMA Tftp
13.6.4 Pointer and References – MMA Tftp
X DNS Facilities
13.7 MMA DNS
13.7.1 Model and Terminology – MMA DNS
13.7.2 Files Overview – MMA DNS
13.7.3 Hints – MMA DNS
13.7.4 Pointer and References – MMA DNS
XI Mail Facilities
14 Email Facilities
14.1 Introduction
14.1.1 General Policies & Procedures
14.1.2 Site Deployment Policies & Procedures
14.2 mmaQmail
14.3 Model and Terminology – MMA Qmail Tools
14.4 Files Overview – MMA Qmail Tools
14.5 Hints – Account Management Tools
14.6 Pointer and References – Account Management Tools
14.7 MMA Qmail
14.7.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Qmail
14.7.2 Files Overview – MMA Qmail
14.7.3 Hints – MMA Qmail
14.7.4 Pointer and References – MMA Qmail
14.8 MMA IMAP
14.8.1 Model and Terminology – MMA IMAP
14.8.2 Files Overview – MMA IMAP
14.8.3 Hints – MMA IMAP
14.8.4 Pointer and References – MMA IMAP
XII Web Facilities
15 Web Server Tools
15.1 opWebServers
15.2 MMA Web
15.2.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Web
15.2.2 Files Overview – MMA Web
15.2.3 Hints – MMA Web
15.2.4 Pointer and References – MMA Web
XIII Database and Directory Facilities
16 Name Services
16.1 nedaIPaddr.sh
16.2 opNetNameServices
17 Directory Services Tools
17.1 Model and Terminology – Directory Services Tools
17.2 Files Overview – Directory Services Tools
17.3 Hints – Directory Services Tools
17.4 Pointer and References – Directory Services Tools
18 Data Base Facilities
XIV Security Facilties
19 Key Management – Remote Access
20 Security Tools
20.1 opSecurity
XV Development and Analysis Tools
21 Development Facilities
21.1 CVS
22 Software Management Tools
22.1 opSwPkgs
23 Performance and Monitoring Tools
XVI Libre Content Production and Publication
24 LaTeX
25 Libre Content Processing
25.1 MMA Published Content
25.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Published Content
25.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Published Content
25.1.3 Hints – MMA Published Content
25.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Published Content
25.2 lcnLcnt
26 Image Processing
27 Video Processing
28 Account Management Tools
28.1 Model and Terminology – Account Management Tools
28.2 Files Overview – Account Management Tools
28.3 Hints – Account Management Tools
28.4 Pointer and References – Account Management Tools
29 Cron and At Tools
29.1 Model and Terminology – Cron and At Tools
29.2 Files Overview – Cron and At Tools
29.3 Hints – Cron and At Tools
29.4 Pointer and References – Cron and At Tools
30 sudo
XVII Common Components – Service and User Environment
XVIII Service Libre Components
31 Printers Management Tools
31.1 opPrHosts
31.2 nedaPrint
32 Voice Over IP (VoIP)
33 Assigned Names and Numbers
33.1 Password File Accounts
33.1.1 Employee Account
33.1.2 Contractor Account
33.1.3 Alumni Account
33.1.4 Associate Account
33.1.5 System Program Accounts
33.1.6 System Program Groups
33.1.7 Subscribers (Authenticated)
33.1.8 QMail Virtual Domain
34 System Management and Configuration
34.1 Introduction
34.2 opSysMgmtActions
34.3 nedaSysMgmtActions
34.4 dotIntra Cluster
XIX User Environment Components
35 ByStar Libre Emacs Office Environment (BLEOE)
36 Wlan Facilities
37 Browser Facilities
XX Native Libre Components
38 VoRDE
38.1 MMA VoRDE
38.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA VoRDE
38.1.2 Files Overview – MMA VoRDE
38.1.3 Hints – MMA VoRDE
38.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA VoRDE
39 LEAP
39.1 MMA EMSD
39.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA EMSD
39.1.2 Files Overview – MMA EMSD
39.1.3 Hints – MMA EMSD
39.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA EMSD
XXI Obsoleted or Deprecated Components
39.2 MMA Jetspeed
39.2.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Jetspeed
39.2.2 Files Overview – MMA Jetspeed
39.2.3 Hints – MMA Jetspeed
39.2.4 Pointer and References – MMA Jetspeed
List of Figures
List of Tables
Part I
Concept and Model
Chapter 1
Open Services Management Tools
1.1 Server To Services Transformation
GNU/Linux demonstrated that large a complete Operating System can be put together purely in the Free Software model.
Various forms of dedicated servers have been integrated based on GNU/Linux. Such server constructs are ad-hoc integrations demanding much expertise.
Collective collaboration towards transformation of ad-hoc servers based on Free Software into mass usable agents for delivery of Libre Services is the next challenge.
Construction of a set of Application Services requires an important extension beyond the underlying software layer. Construction of a set of Application Services requires the integration of a set of software components together to provide useful functionality to the user.
This integration layer must conform to correct principles of structure and consistency. Thus Free Services represent an extension of the Free Software model based on structured and consistent integration.
The versatile “Glue” needed to bring about the needed structure and consistency is a crucial element for realization of Libre Services. Much effort has been devoted to creation of the initial implementation of this Glue. See “Open Systems Management Tools”, [?] for more details.
1.2 Open Services Management Tools
OSMT (Open Services Management Tools) are a set of tools on top of which various consistent polices can be implemented.
This is a collection tools that collectively lets you consistently manage Unix and Linux systems and some of the tools will also manage Windows system.
1.3 GOALS
Key goals for the design has been:
- Be very Unix centric. Focus on Solaris and Linux
- Limit use of the tools to what is minimally and genericly available on plain Unix systems. Namely Korn Shell.
- Be consistent in use of the tools. View this work as a collection. Not bits and pieces here and there.
- Don’t view the tools as host management tools, view them as domain management and system management tools.
- Support consistent and simultaneous management of multiple domains. Detection of Sites, Domains and Hosts is an integral part of these tools.
- Tools should be location independent.
1.4 Common Features
The following features are available to all scripts based on
seedActions.sh and seedSubjectActions.sh
Tracing: -T <runLevelNumber> -- Ex: mmaQmailHosts.sh -T 9 ...
Run Mode: -n <runMode> -- Ex: mmaQmailHosts.sh -n runSafe ...
Verbose: -v -- Ex: mmaQmailHosts.sh -v
Force Mode: -f -- Ex: mmaQmailHosts.sh -f
Check Mode: -c -- Ex: mmaQmailHosts.sh -c fast
Tracing
=======
DEFAULT: -T 0
Trace Number Conventions:
0: No Tracing
1: Application Basic Info
2: Application General Info
3: Application Function Entry and Exit
4: Application Debugging
5: Wrappers Library
6: Seed Script
7: Seed Supporting Libraries (eg, doLib.sh)
8: ocp_library
9: Quick Debug, usually temporary
Run Mode:
=========
DEFAULT: runOnly
G_runMode=
showOnly: at opDo⋆ just show the args always return 0
runOnly: at opDo⋆ just execute
showRun: at opDo both runOnly and showOnly
runSafe: at opDo both show and run, but if protected
then just show
showProtected: Run everything and don't show except for
show only protected
showRunProtected: Run everything and don't show except for
run and show rotected
runSafe = unprotected: showRun, protected: show
showProtected = unprotected: run, protected: show
showRunProtected = unprotected: run, protected: showRun
Verbose Mode:
=============
G_verbose=
verbose When Set, verbose format (eg, line nu, time tag, ...)
of Tracing and RunMode are selected.
Force Mode:
=============
G_forceMode=
force When Set, force/overwrite mode of operation
is selected.
Check Mode:
===========
G_checkMode={fast,strict,full}
fast: 1) Skip asserting and consistency checks.
2) Do less than default, invoker will
compensate
strict: Do asserts and consistency checks.
full: 1) Do more than default
1.5 Obtaining LSIP
http://www.neda.com/libre/lpGenesis.sh
1.6 LSIP License
Afero GPL V3.
1.7 LSIP Overview
Take from presentation.
Part II
Libraries and Seeds
1.8 Libre Platform Definitions
Part III
Libre Platform Base
Chapter 2
Open Platform Libraries
2.1 doLib
The doLib.sh is a place for common features for script that used the seedSubjectAction. This common features includes:
vis_ls | list all of the functions (hence, equivalent to items) inside the itemsFile. |
do_list |
|
do_describe | describing each items in the itemsFile if opItem_description function exist within the item. |
do_itemActions | if the item has a list of itemActions, then it will perform all of them. |
doLibExamplesOutput | list all of the common examples for the seedSubjectAction script which include common examples (showMe, seedHelp, ls, list, describe) and common debugging. |
To use this feature, put the following in each of the seedSubjectAction script:
function vis_examples {
typeset doLibExamples=‘doLibExamplesOutput ${G_myName}‘
cat << _EOF_
EXAMPLES:
${doLibExamples}
--- EVERYTHING ELSE
.....
.....
.....
_EOF_
}
2.2 visLib
This library function the same as doLib except this lib is for seedActions script.
2.3 ocp-lib
The ocp-lib loads all of the osmt library. Each of these libraries will be covered in the following sections.
2.4 ocp-general
ocp-general is a collection of several functions which can be used by any scripts. This library will most probably grow over time to simplify tasks.
Function name convention:
- MA_: mail addressing parsing
- ATTR_: Attribute value parsing
- FN_: File Name Manipulation
- USER_: passwd file related activities
- PN_: Path name
The functions included in this library are:
| MA_domainPart | Mail address parsing. Print out the domain part. Example: MA_domainPart vendors@neda.com will output neda.com. |
| MA_localPart | Mail address parsing. Print out the local part. Example: MA_localPart vendors@neda.com will output vendors. |
| ATTR_leftSide | Attribute value parsing. Print out the left side of the equal sign (=). Example: ATTR_leftSide variable1=value1 will output variable1. |
| ATTR_rightSide | Attribute value parsing. Print out the right side of the equal sign (=). Example: ATTR_rightSide variable1=value1 will output value1. |
| FN_prefix | Print out only the basename of a file without the extension. Example: FN_prefix /opt/public/osmt/bin/mmaQmailHosts.sh will output mmaQmailHosts. |
| FN_extension | Print out only the extension of a basename file. Example: FN_extension /opt/public/osmt/bin/mmaQmailHosts.sh will output sh. |
| FN_dirsPart | Print out only the directory of a specific file location. Example: FN_dirsPart /opt/public/osmt/bin/mmaQmailHosts.sh will output /opt/public/osmt/bin. |
| FN_nonDirsPart | Print out only the basename of a specific file location. Example: FN_nonDirsPart /opt/public/osmt/bin/mmaQmailHosts.sh will output mmaQmailHosts.sh. |
| FN_fileDefunctMake | Make a specific file become no longer active in the system by moving the file into another file and chmod to 0000. It requires 2 arguments. First arg is the name of the file that we want to defunct and second arg is the new name and it should not have existed. |
| FN_dirDefunctMake | Same as the above except it applies to a directory instead of a file. |
| FN_FileCreateIfNotThere | Create a null file if it does not exist. |
| FN_dirCreateIfNotThere | Create a directory if it does not exist using the mkdir command. |
| FN_dirCreatePathIfNotThere | Create a directory path if it does not exist using mkdir -p command. |
| FN_fileSymlinkSafeMake | Requires 2 arguments: source/origin of a file (should exist)and the target name. If the target exist, skip the symlink process. |
| FN_fileSymlinkUpdate | Same as FN_fileSymlinkSafeMake except if the target exist, it will remove the old symlink and make a new one. |
| FN_fileSafeCopy | Required 2 arguments: a source name and a target name. If the target exist, it will skip the copy process. |
| FN_fileCopy | Same as FN_fileSafeCopy except if the target exist, it will overwrite the old file. Use with caution. |
| FN_fileSafeKeep | Move a file and rename it with a dateTag extension. |
| FN_dirSafeKeep | Move a directory and rename it with a dteTag extension. |
| FN_lineIsInFile | Required 2 arguments: string to check and the filename. It will return 0 if the string is found in the file specified and 1 otherwise. |
| FN_lineAddToFile | Required 3 arguments: string to check, string to be added, the filename. |
| FN_textReplace | Required 3 arguments: regexp of text to replace, replacement text, and
the filename. The regexp of text to replace has to be in the format of 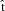 ext.*$. ext.*$. |
| FN_textReplaceOrAdd | If the text to be replaced exist in the file, it will call FN_textReplace otherwise the replacement text will be added to the file. |
| FN_fileInstall | This is to ensure that we use FSF’s install command. In SunOS the location is in /opt/sfw/bin/install. |
| FN_grep | This is to ensure that we use grep command that supports ”-F”, ”-v”, and ”-q”. In SunOS, the location is /usr/xpg4/bin/grep. |
| FN_egrep | This is to ensure that we use egrep command that support ”-v”, ”-q”. |
| _opDoRunOnly | |
| _opDoShowOnly | |
| _opDoShowRun | |
| _opDo | |
| _opDoAssert | |
| opDoProtectedBegin | |
| opDoProtectedEnd | |
| opDoProtected | |
| USER_isInPasswdFile | Return 0 if a user is in the /etc/passwd file. |
| USER_loginGivenHomeDir | Required 1 argument: the path to home directory. If the home directory is found in /etc/passwd, it will output his/her loginName and return 0 otherwise it will return 1. |
| USER_nextLoginNameGet | .... |
| PN_fileVerify | List information about file. |
| FN_fileRmIfThere | Calling PN_rmIfThere. |
| PN_rmIfThere | If -v is specified, it will enable the verbose mode. You can specified more than 1 file to be removed. |
| IS_inList | Required 2 arguments: a string to be checked and a list of strings. Return 0 if the string is in the list of strings otherwise return 1. |
| LIST_getLast | Get the last argument/string in a list. |
| LIST_getFirst | Get the first argument. |
| LIST_set | |
| LIST_minus | |
| LIST_setMinusResult | |
| doStderrToStdout | Put standard error to standard output. |
| G_validateOption | Required 2 arguments: target and a list. If the target is in the list, it will set targetIsValid=”TRUE”. |
| G_abortIfNotSupportedOs | Abort the running script if the OS is not supported. The currently supported OS are SunOS and Linux. |
| G_abortIfNotRunningAsRoot | Abort the running script if the current user is not root. |
| G_returnIfNotRunningAsRoot | Return 1 if the current user is not root. |
| G_validateRunOS | Required 1 argument: a list of OS. If the current OS is in the given list, it will set isValid=”TRUE” otherwise it will set isValid=”FALSE” and exit. |
| DOS_toFrontSlash | Convert DOS filename to UNIX system filename. |
| DOS_toBackSlash | |
| RELID_extractInfo | Information about product’s release ID |
| logActivitySeparator | |
| buildAndRecord | |
2.5 ocp-lineNu
This library contains functions for debugging purposes.
tm_trace | Depending on what the trace level is, will print out information for debugging purposes. For more complete information, see section ??. |
log_event | For loging purposes. |
eh_problem | Give out PROBLEM message and continue. |
eh_fatal | Give out a FATAL message and exit. |
2.6 ocpLibUse
2.7 opRunEnvLib
To setup and verifying the environment configuration on the system.
2.8 opWrappersLib
This script includes these functions:
opNetCfg_paramsGet | Required 2 parameters: clusterName and hostName. Given these 2 parameters, the nedaIPaddr.sh is called and the network setting for this particular cluster and hostname are set. |
i_nedaNetParamsGet | Used by the opNetCfg_paramsGet to set all of the network setting as global variables. These global variables are: opNetCfg_ipAddr, opNetCfg_domainName, opNetCfg_netmask, opNetCfg_networkAddr, opNetCfg_defaultRoute. |
2.9 itemsLib
itemsLib ia a set of facilities that operate on any item files.
| |
opItem_description | Whenever -i describe is executed, it will call opItem_description and this function will look for iv_descriptionFunction in each of the item in the itemsFile. If it exist, the description will be printed out. |
opItem_selectClusterFiles |
|
opItem_ifAvailableInvoke |
|
opItem_isAvailable | It will check whether the item is available to hostMode (by calling opItem_isAvailableToHostMode) and if it is within the cluster (by calling opItem_isWithinClusterScope). It will return 0 if everything is correct. |
opItem_isAvailableToHostMode |
|
opItem_isAvailableToOs |
|
opItem_isWithinClusterScope | Subject variables should be all set (iv_itemScopeVisibleHosts, iv_itemScopeVisibleClusters, iv_itemScopeHiddenHosts). Returns:
0 if disk within scope and should be acted upon
1 if disk is tagged to be hidden 2 if disk not in the cluster and also not tagged as visible
|
2.9.1 Visibility Rules
2.9.1.1 items Visibility
By adding
item is visible to
iv_itemScopeVisibleClusters -- List of clusters, item is visible to
iv_itemScopeHiddenHosts -- List of hosts inside of the clusters
item is visible to
you can then use opItem_isWithinClusterScope to check the visibility of the item.
By adding
you can then use opItem_isAvailableToHostMode.
By adding
iv_itemAvailableToMachineArch -- matched against opRunMachineArch
you can then use opItem_isAvailableToOs.
2.9.1.2 runMode Visibility
2.9.1.3 Cluster Visibility
2.9.1.4 Binary Visibility
2.10 opDoAtAsLib
Chapter 3
Seed Scripts
3.1 seedActions.sh
3.1.1 Description
seedAction.sh
DESCRIPTION
seedActions.sh is the basis of a tool for grouping
a number of functions within a shell script and allowing
for their execution and maintenance in a consistent way.
A large number of common features are provided by simply
loading seedActions.sh. seedActions.sh integrates itself
with your script in three stages.
Below is the diagram of how this seedActions.sh works:
seedActionsExample.sh | seedActions.sh
|
1 | |
| |
+-------------------+--------------+ Configuration set:
| - opConfig.sh
| | Library load:
| A | - ocp.lib
| | GETOPT
+-------------------+--------------+
2 | |
Default + | |
Mandatory | |
Parameters | |
+-------------------+--------------+
| | Set the user
| B | define parameters
POST | |
+-------------------+--------------+
3 | |
vis_ | |
functions | |
+-------------------+--------------+
| | Execute
| C | tasks
| +
In this description, the routine is:
part 1 called --> part A executed -->
part 2 called --> part B executed -->
part 3 called --> part C executed.
First, mmaExampleActions.sh is calling part 1:
if [ "${loadFiles}X" == "X" ] ; then
seedActions.sh -l $0 $@
exit $?
fi
As a result, the seedActions.sh is executed and
the first thing that seedActions.sh do is execute Part A:
- load opConfig.sh
- load ocp-lib.sh (OCP Library)
- process GETOPT (get options)
After Part A is executed, mmaExampleActions.sh declare the
default parameter with tags (typeset -t) if any.
This is also known as PRE loading.
typeset -t FirstName=MANDATORY
typeset -t LastName=MANDATORY
typeset -t SubsSelector=""
.....
This is where all of the necessary parameters are set,
including the default and mandatory parameters.
parameter=value from the command line must match a
typeset -t.
The initial value of mandatory variables is MANDATORY
After all the parameters are set, seedActions.sh
executes Part B:
- set all of the user's define parameters.
After we have all the parameters, part 3 is called
(POST Loading). Part 3 only executed if function
called G_postParamHook exist within the script.
command line "someFunction" maps to function: vis_someFunction
OPTIONS
All scripts base on seedActions.sh get getopts with the
following options:
-T traceLevel Use for debuging purposes -- tracing,
with traceLevel being a number
between 0-9.
-i Run a specific visible function within the
script.
-p Specify the required/default parameters.
parameter=value from the command line must match a
typeset -t. For example:
-p FirstName=Homer ...
-l Specify the file for loading.
-u Gives USAGE Info. The usage info automatically
lists all visible functions without the prefix "vis_".
VISIBLE FUNCTIONS
- The visible functions (indicated by prefix vis_) are internal
functions which are exposed externally.
- It can accept ARGS on command line.
CONVENTIONS
- In every script, vis_help is always put on top.
The idea being that a description of the script
can always be accessed through "-i help" in the
command line.
- Those based on seedActions.sh should end in a category
of actions as a VERB. The most generic form is the verb
Action itself. For example: mmaSendmailAction.sh
- The noArgsHook function will be available in some
of the script.
If a default action is applicable to a script,
the noArgsHook is called, if it exists,
based on the recognition that a default action will be
performed.
If noArgsHook is not specified and the script is run with
no options, then this warning will be displayed:
"No action taken. Specify options. See -u"
EXAMPLE
Mandatory parameters:
the initial value of mandatory variables is MANDATORY
e.g.
typeset -t FirstName=MANDATORY
In order to force this parameter to be set (hence MANDATORY)
call the opParamMandatoryVerify within the function
that needs this parameter. When opParamMandatoryVerify is
executed, it will check all of the parameters that has initial
value MANDATORY. If it is not set, return error.
Optional parameters:
the optional parameters has initial value other that MANDATORY.
vis_help: the vis_help can always be accessed through "-i help"
in the command line
Example of usage: anyScript.sh -i help
Example of code:
vis_help () {
cat << _EOF_
Put any text here for information related to this script.
_EOF_
exit 1
}
noArgsHook:
e.g.
noArgsHook="noArgsHook"
noArgsHook() {
# If no args, default action or usage
if [ "$⋆X" == "X" ]
then
echo "No Defaults Specified"
echo "Specify Options -- See -u for list of visible actions"
usage
fi
}
3.1.2 Example
Take a look at mmaExamplesActions.sh
3.2 seedSubjectAction.sh
3.2.1 Description
seedSubjectAction.sh
DESCRIPTION
seedSubjectAction.sh is the basis of a tool for grouping
a number of functions within a shell script and allowing
for their execution and maintenance in a consistent way.
A large number of common features are provided by simply
loading seedSubjectAction.sh. seedSubjectAction.sh integrates itself
with your script in three stages.
Below is the diagram of how this seedSubjectAction.sh works:
procSubjects.sh.sh | seedSubjectAction.sh | procSubjectItems.main
| |
1 | | |
| | |
+-----------+--------------+ Conf. set: |
| | - opConfig.sh |
| | Library load: |
| A | - ocp.lib |
PRE | | GETOPT |
+-----------+--------------+ |
2 | | |
Default + | | |
Mandatory | | |
Parameters | | |
+-----------+--------------+ |
| | Set the params |
| B | |
POST | | |
+-----------+--------------+ |
3 | | |
do_ | | |
item_ | | |
functions | | |
itemFiles +-----------+--------------+ |
specified here | | |
| +----------------+-------+
| | | procSubjectItems.
| +----------------+-------+
| | |
| C +----------------+-------+
| | | procSubjectItems. N
| +----------------+-------+
| | |
| | |
| + |
In this description, the routine is:
part 1 called --> part A executed -->
part 2 called --> part B executed -->
part 3 called --> part C executed.
First, seedSubjectActionExample.sh is calling part 1:
if [ "${loadFiles}X" == "X" ] ; then
seedSubjectAction.sh -l $0 $⋆
exit $?
fi
As a result, the seedSubjectAction.sh is executed and
the first thing that seedSubjectAction.sh do is execute Part A:
- load opConfig.sh
- load ocp-lib.sh (OCP Library)
- process GETOPT (get options)
After Part A is executed, seedSubjectActionExample.sh declare the
default parameter with tags (typeset -t) if any.
This is also known as PRE loading.
if [ "${loadSegment}_" == "PRE_" ] ; then
# Mandatory parameters
typeset -t VirDomRoot=MANDATORY
typeset -t VirDomTLD=MANDATORY
# Optional parameter = default value
typeset -t SiteName=xyzPlus
.....
This is where all of the necessary parameters are set,
including the optional and mandatory parameters.
parameter=value from the command line must match a
typeset -t.
The initial value of mandatory variables is MANDATORY
and the optional parameters become the default value.
After all the parameters are set, seedSubjectAction.sh
executes Part B:
- set all of the user's define parameters.
After we have all the parameters, part 3 is called
(POST Loading). Part 3 only executed if function
called G_postParamHook exist within the script.
The setBasicItemsFile is called here. See CONVENTIONS
section for how setBasicItemsFiles works.
The itemsFile are loaded from the procSubjectItems file:
procSubjectItems.<specificCluster>
where procSubjetItems is the corresponding procSubjects.sh,
<specificSite> is one of main, office, public, etc.
When procSubjectItems is executed, itemPre and itemPost
are defined, if there is any.
itemPre is a place where all the default and mandatory
parameters are specified.
itemPost derived defaults.
After the itemsFile is loaded, "subject" and "action"
are defined.
command line "subject" maps to function: item_subject
command line "action" maps to function: do_action
By convention, it calls itemAction_action.
OPTIONS
All scripts base on seedSubjectAction.sh get getopts with the
following options:
-T traceLevel Use for debuging purposes -- tracing,
with traceLevel being a number
between 0-9.
-a Run the specific action. The "action"
automatically lists all the action available
without the "do_" prefix.
Also applies to itemCmd_ as well.
-s Apply the -a "action" to a specific "subject".
The "subject" automatically lists all the subject
available without the "item_" prefix.
-i Run a specific visible function within the
script.
-p Specify the required/default parameters.
parameter=value from the command line must match a
typeset -t. For example:
-p FirstName=Homer ...
-l Specify the file for loading.
-u Gives USAGE Info. The usage info automatically
lists all visible functions without the prefix "vis_".
CONVENTIONS
- In every script, vis_help is always put on top.
The idea being that a description of the script
can always be accessed through "-i help" in the
command line.
- Those based on seedSubjectAction.sh should end
in the plural of the OBJECT, if there are categories
of actions related to the objects those as verbs come
before the plural of the object.
For example: opDiskDrives.sh or mmaQmailHosts.sh
The seed of the items file is the singular of the fileName
plus Items. For example opDiskDriveItems.sh or mmaQmailHostItems.sh.
- The noArgsHook function will be available in some
of the script.
If a default action is applicable to a script,
the noArgsHook is called, if it exists,
based on the recognition that a default action will be
performed.
If noArgsHook is not specified and the script is run with
no options, then this warning will be displayed:
"No action taken. Specify options. See -u"
- The noSubjectHook function will be available in some
of the script.
This function will be executed if there is no subject
specified.
- The firstSubjectHook and lastSubjectHook are typically
used when the subject is all. Most of the time, it will
be used for printing summary of the itemsFile.
- setBasicItemsFiles procSubjectItems
Here are the flow how setBasicItemsFiles works:
if there is procSubjectItems.main, then add it.
if there is procSubjectItems.clusterName, then add it.
if there is none of the above then
if there is procSubjectItems.site, then add it.
if there is procSubjectItems.otherName, just ignore it.
Here is a scenario:
- For example, suppose we have all of these files:
procSubjectItems.main, procSubjectItems.office,
procSubjectItems.home, procSubjectItems.otherCluster
and we are running from an office machine environment
then only procSubjectItems.main and procSubjectItems.office
are loaded and the other are ignored.
- The itemsFile policy:
item_SSSS (SSSS is the subject)
itemPre
iv_specialize
itemPost
itemCmd_
- Built in function:
list -- built in action
all -- built in subject
Example of use in command line:
anyScript.sh -s all -a list
This command will enumerate all the subject item_ entries from
the ItemsFile and list all of the paramaters corresponding to
each subject item_.
EXAMPLE
Mandatory parameters:
---------------------
the initial value of mandatory variables is MANDATORY
e.g.
typeset -t FirstName=MANDATORY
Optional parameters:
--------------------
typeset -t FirstName=homer
vis_help:
---------
the vis_help can always be accessed through "-i help"
in the command line
Example of usage: anyScript.sh -i help
Example of code:
vis_help () {
cat << _EOF_
Put any thext here for information related to this script.
_EOF_
exit 1
}
noArgsHook:
-----------
e.g.
noArgsHook="noArgsHook"
noArgsHook() {
# If no args, default action or usage
if [ "$⋆X" == "X" ]
then
echo "No Defaults Specified"
echo "Specify Options -- See -u for list of visible actions"
usage
fi
}
Use of parameters in vis_ function:
-----------------------------------
print ${FirstName} will give result "homer".
ItemsFile Selection:
--------------------
There are 2 ways to load the procSubjectItems:
1. Automatic ItemsFile Selection
setBasicItemsFiles procSubjectItems
2. Manual ItemsFile Selection
ItemsFile=${opSiteControlBase}/${opSiteName}/procSubjectItems.main
do_ description:
----------------
The do_AAA function is the AAA "action" taken to some
"subject" item_.
By convention it calls itemAction_AAA.
itemCmd_ description:
---------------------
3.2.2 Example
Take a look at mmaExamplesObjects.sh
Part IV
Base Platform and Site Abstraction
Chapter 4
Site and Clusters Selection
HOST MODE CLUSTER NAME ACTION
+------------+-------------+--------------------------------------+
| | Unclustered | Segments local & no mount |
| Unnet +-------------+--------------------------------------+
| | SomeCluster | Illegal |
+------------+-------------+--------------------------------------+
| | Unclustered | Segments local & no mount |
| StandAlone +-------------+--------------------------------------+
| | SomeCluster | if opRunParamStandAlone is |
| | | - strict: Segments local & no mount |
| | | - cluster: Segments local & mount |
+------------+-------------+--------------------------------------+
| | Unclustered | Illegal |
| Cluster +-------------+--------------------------------------+
| | SomeCluster | Mount & links |
+------------+-------------+--------------------------------------+
belong to are as follows:
1. Find out which SiteName the systemName belong to.
2. Knowing which siteName, search for host.
3. Knowing the hostName, search for clusterName.
4. Knowing the clusterName, search for Domain.
There are several possible cluster names:
1. office
2. island
3. dmz
4. payk
5. subscriber
6. test
7. public
8. unclustered
And there are several possible opHostMode:
1. UnNet (U)
2. Standalone (S) -- no mount
3. Clustered (C)
4. SelfContained (SC) -- mount but no symlink
4.1 opHosts
4.2 opSites
4.3 opClusters
4.4 opDomains
4.4.1 opSysIdentities
Chapter 5
Conventions
5.1 Introduction
5.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Tools
Extracted by mmaRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
Manipulative Verbs:
-------------------
itemShow -- displays the subject [pkgShow -- when pkgManipulators]
compShow -- displays (Componenet) what is in the system
verify -- compares subject and system
update -- makes system same as subject
delete -- removes from system
NetListener
-----------
A Net Listner is network responder dispatched
upon a connection request establishment.
Facilities dispatching Net Listners are:
- inetd
- ucspi
- tcpwrapper
A NetListener can also be a daemon.
NetListener Modes
----------------
- enabled -- active and responding
- disabled -- inactive will not respond
- standby -- active but should not be first in dns list
--- NETLISTENER ACTIONS ---
mmaRoadmap.sh -s tehran -a netListenerEnable
mmaRoadmap.sh -s tehran -a netListenerDisable
mmaRoadmap.sh -s tehran -a netListenerShow
mmaRoadmap.sh -s tehran -a netListenerVerify
Network Services Verbs (inetd and daemons)
------------------------------------------
netListenerEnable -- inetd add line and HUP
-- For daemons upon reboot serviceStart
-- For daemons serviceStart
netListenerDisable -- inetd delete line and HUP
-- For daemons upon reboot no action
-- For daemons serviceStop
netListenerShow -- inetd delete line and HUP
netListenerVerify -- inetd delete line and HUP
Daemon Services Verbs
---------------------
serviceStart -- init.d/xxx start
serviceStop -- init.d/xxx stop
serviceRestart -- init.d/xxx restart
Qualifiers to Manipluative Verbs:
---------------------------------
-f G_forceMode:
-v G_verboseMode:
-c G_checkMode
FULL MANIPLUATORS:
fullVerify -- compares subject and system
fullUpdate -- makes system same as subject
fullDelete -- removes from system
fullStop -- Stops ALL services for subject
fullStart -- Starts ALL services for subject
BinsPrepConventions:
--------------------
- see mmaBinsPrep.sh
Top Level Facilities:
---------------------
opSysIdentities.sh
opSysMgmtActions.sh
mmaSysMgmtActions.sh
bynameSysMgmtActions.sh
5.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Tools
Extracted by mmaRoadmap.sh -i help
5.1.3 Hints – MMA Tools
Extracted by mmaRoadmap.sh -i howTos
C: How Do I Setup a mailing list?
5.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Tools
Extracted by mmaRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Mma man pages.
Part V
Package and Distribution Facilities
Chapter 6
Linux Distribution Abstractions
Chapter 7
BinsPrep
Chapter 8
Operating System Installation
8.1 opGenesis
See PLPC-110101.
Part VI
Host and Site Administration
Chapter 9
Disk Management Tools
This tools are used to keep track/manage all kinds of tasks related to disk
drives.
The sort of tasks that this tool performed are:
- ItemsFile: opDiskDriveItems.site. This items file keep tracks the disk drives hardware – each disk drive is assigned a
letter. Most of them are external drive. In some cases, if the internal disk is large (i.e. more than 2GB) then it will be
assigned a letter. The information in this file is as follow (as an example):
iv_dd_itemName="a"
iv_dd_diskInfoPartitionCapacity="2GB"
iv_dd_diskShareWith="root swap /export/home"
iv_dd_diskInfoDrive="External"
iv_dd_diskInfoAssetLocation="C8-02-03.02"
iv_dd_diskSerialNumber="621G1815"
- ItemsFile: opDiskDriveUseItems.site. This items file keep track of the usage of each partition of the disk drive. The
purpose of this is to mount the partition on another system. The information in this file is as follow (as an
example):
iv_du_itemName=${0##item_du_}
iv_diskHostMountPoint="/i1"
iv_diskUsageMountPoint="/i1"
iv_diskHost="jamshid"
iv_diskPurpose="data"
iv_itemScopeVisibleHosts=""
iv_itemScopeHiddenHosts=""
iv_itemScopeVisibleClusters="office"
iv_diskSCSItarget=1
iv_diskPartitionNu=2
iv_diskPartitionSize="18GB"
iv_diskPartitionSylBegin="0"
iv_diskPartitionSylEnd="35368271"
If the iv_itemScopeVisibleClusters is “uncluster” then this partition will not be mounted anywhere at all. The iv_itemScopeHiddenHosts will only apply to the system in the same cluster and iv_itemScopeVisibleHosts will only apply to the system in different cluster.
- ItemsFile: opDiskSegmentItems.site. This items file is used for symlink purposes. Visibility applies to multiple hostMode.
The hierarchy of the disk management is depicted in this figure:
+-------------------------+
| opDiskSegmentItems.site | SYMLINK PURPOSES
+-------------------------+
+--------------------------+
| opDiskDriveUseItems.site | MOUNTING PURPOSES
+--------------------------+
+-----------------------+
| opDiskDriveItems.site | HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
+-----------------------+
9.1 Model and Terminology – Disk Management Tools
Extracted by opDisksRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
opDisksRoadmap.sh -- Documentation
opDiskDrives.sh -- Abstraction of a physical
disk drive. Include
- Disk Name (v)
- Type Internal/External
- Size
- Asset reference
- ...
Gets included (doted) by
diskDriveUses.sh
The types of things that
can be done are:
⋆ summaries
opDiskDriveUses.sh -- How a particular disk drive
is being used.
- Which Host is using
- At what mount point
- With what partitions
Subject to visibility rules.
The types of things that
can be done are:
⋆ localMount
⋆ remoteMount
⋆ export
⋆ summaries
opDiskSegments.sh -- Abstraction of a segment
of a disk drive used for a
particular purpose.
The types of things that
can be done are:
⋆ symLinks
⋆ backup
⋆ replications/synchronization
opDiskBackupServers.sh -- backupSchedule, summaries
mmaRsyncDiskSegments.sh -- Rsync, ...
ITEM FILES
----------
- opDiskSegmentItems.main
- opDiskSegmentItems.{diskName} -- e.g., t1
- opDiskSegmentPkgItems.{pkgName} -- e.g., pubBasics
- opDiskSegmentImportItems.{diskName} -- e.g., k1
- opDiskSegmentItems.{diskName} includes:
- visibility information, for the purpose
deciding to whether or not a certain item
is visibile given the host/cluster/mode
information.
If not visible, the entire item is ignored.
- segement self information.
- import information
- export parameters, including
export/back-up frequency.
- opDiskSegmentPkgItems.{pkgName} is a bounch of
segements which are to be identical on each
diskSegemenItems.{driveName} file which includes
them.
- opDiskSegmentImportItems.{diskName} includes
information for how to import/export segments on a disk
being exported/imported by a particular host.
loading of the container may be repeated within
each item. Each item refers to its own exporter.
To distinguish whether a segment is meant to be:
- an importer (meaning it can only RECEIVE from the outsider),
it determined by iv_dsImport_methodsList and set
iv_dsImport_exporterMethodsList to nul.
- an exporter (meaning it can only SEND OUT to the outsider),
it determined by iv_dsImport_exporterMethodsList and set
iv_dsImport_methodsList to nul.
- an exporter AND an importer set both parameter.
rsyncSshPush and rsyncSshPoll
=============================
Push
+---------<<<<<<<<<<-------------+
| |
v |
+----------+ +----------+
| IMPORTER | | EXPORTER |
+----------+ +----------+
| ^
| |
+---------->>>>>>----------------+
Poll
IMPORT ACTION
-------------
if the iv_dsImport_methodsList is "rsyncSshPoll" then the action
(segmentsImport) can only be run from the importer site.
The importer REQUEST DATA from the exporter (Import From).
<Kind of Remote to Local Rsync>
EXPORT ACTION
-------------
if the iv_dsImport_exporterMethodsList is "rsyncSshPush" then the action
(segmentsExport) can only be run from the exporter site.
The exporter PUSH DATA to the importer (Export To).
<Kind of Local To Remote Rsync>
if the iv_dsImport_exporterMethodsList is "rsyncSshPoll" then
the importer may request data from the exporter.
DISKS BACKUP/MIRROR
===================
opDiskBackupServers.sh can be used to backup or
mirror any disks. Most of the works are done through
opDiskSegments.sh. The difference between backup and
mirror operation is in the destination's directory
structure.
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Source | Operation | Destination |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| /x1/opt/public/osmt | mirror | /a1/opt/public/osmt |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| /x1/opt/public/osmt | backup | /backups/030220124157/x1/opt/public/osmt |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Related files:
--------------
opDiskDriveUseItems.site -- opDiskSegments.sh use these items file
for its subject (i.e -s du_x1)
In each of the item, there is
iv_du_segmentsFileRef and it will
refer to opDiskSegmentItems.xx
opDiskSegmentItems.xx -- xx is the disk label (e.g. x1,i1, etc)
Contain information for import/export
disk segments as well as backup frequency.
opDiskSegmentPkgdItems.pubBasics -- Contain disk segments that are common
for all disk.
opDiskSegmentImportItems.xx -- xx is the disk label (e.g. x1,i1, etc)
Contain disk segment that can be used for
import/export. This file is used by
importer. So if the segments is in this
file, the importer can then import this
segment.
opDiskBackupServerItems.office -- Contain backup server info.
opDiskBackupServers.sh actions
------------------------------
exportBackup: exporting a segment to remote backup server.
importBackup: importing a segment to be backuped from a remote host.
Whether a segment need to be backuped or not
is determined by the backup frequency.
If backupFreq is "NONE" then the segment is not subject to
backup.
9.2 Files Overview – Disk Management Tools
Extracted by opDisksRoadmap.sh -i help
9.3 Hints – Disk Management Tools
Extracted by opDisksRoadmap.sh -i howTos
Q: How Do I Setup a new disk and prepare it for
backup?
A: 1. Add new items file to opDiskDriveUseItems.site
For example: item_du_x1 where x1 is the
new disk label.
2. Create new file named opDiskSegmentItems.x1
If x1 will have all of the disk segment listed in
the pkgdItem.pubBasics, do loadPkgd_pubBasics.
If x1 will have custom segments, add it to this file.
See example of this custom segments in
opDiskSegmentItems.v1. Set the backup frequency.
3. If x1 will be used by other disk to import
disk segment from it, create opDiskSegmentImportItems.x1
file.
9.4 Pointer and References – Disk Management Tools
Extracted by opDisksRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Mma man pages.
Part VII
Disk and Storage Facilities
Part VIII
System Foundation Facilities
9.5 MMA Daemon Tools
9.5.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Daemon Tools
Extracted by mmaDaemontoolsRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
- svscan start/stop through /etc/init.d/
Per Service Actions
===================
mmaDaemon{Update,Delete,List,Start,Stop,...}
available through the library.
9.5.2 Files Overview – MMA Daemon Tools
Extracted by mmaDaemontoolsRoadmap.sh -i help
9.5.3 Hints – MMA Daemon Tools
Extracted by mmaDaemontoolsRoadmap.sh -i howTos
9.5.4 Pointer and References – MMA Daemon Tools
Extracted by mmaDaemontoolsRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Part IX
Network Foundation Facilities
Chapter 10
L2 Facilities
Chapter 11
L3 Facilities
11.1 MMA Layer 3
11.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Layer 3
Extracted by mmaLayer3Roadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
- subnetworks:
- interfaces:
Objects Overview:
-----------------
item_l3_server_{HostName}: Config Parameters for the router.
mmaLayer3 Object Processors and Containers:
------------------------------------------
mmaLayer3Hosts.sh
11.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Layer 3
Extracted by mmaLayer3Roadmap.sh -i help
mmaLayer3 (MailMeAnywhere LAYER3) is a set of consistent
policies built on the LAYER3 as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
mmaLayer3 Commands, each contain a set of related functions
which allow you to accomplish specific tasks. Specifically:
COMMAND TYPE USED BY
mmaLayer3.sh action.sh any
mmaLayer3Lib.sh library.sh root/any
mmaLayer3BinsPrep.sh action.sh root
mmaLayer3Hosts.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaLayer3Admin.sh action.sh root/any
At A Glance
-----------
Basic layer3
-----------
mmaLayer3.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaLayer3Lib.sh -- To be included in all mmaLayer3 scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaLayer3BinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for layer3/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
mmaLayer3BinsInstall.sh -- Install mmaLayer3 binaries on opRunHostName
mmaLayer3Hosts.sh -- For subject host, configure layer3
11.1.3 Hints – MMA Layer 3
Extracted by mmaLayer3Roadmap.sh -i howTos
Config Device Driver Modules -- Net Devices
Ferm -- Firewal to iptables high level compiler
Band Width Monitor -- NOTYET
IP Forwarding enabled/disabled
Through /etc/sysctl.conf
add the following
net/ipv4/ip_forward=1
Bring Up/down Interfaces
ifup
ifdown
ferm generates iptables enteries
What does iptables -t net -L do?
setup_fw?
Load kernel modules #3C59X VoRTEX
11.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Layer 3
Extracted by mmaLayer3Roadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Layer3: http://
Chapter 12
UCSPI
12.1 MMA Ucspi
12.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Ucspi
Extracted by mmaUcspiRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
svs
12.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Ucspi
Extracted by mmaUcspiRoadmap.sh -i help
12.1.3 Hints – MMA Ucspi
Extracted by mmaUcspiRoadmap.sh -i howTos
12.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Ucspi
Extracted by mmaUcspiRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Chapter 13
Misc
13.1 MMA FTP
13.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA FTP
Extracted by mmaFtpRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
13.1.2 Files Overview – MMA FTP
Extracted by mmaFtpRoadmap.sh -i help
DESCRIPTION
mmaFtp is a set of consistent facilities
on top of wu-ftp which enforces MMA policies.
Basic DNS Scripts
-----------------
mmaFtp.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaFtpBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for djbFtp
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
-- Install mmaFtp binaries on opRunHostName
mmaFtpHosts.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
mmaFtpAdmin.sh -- Start, stop and addNewAccounts
13.1.3 Hints – MMA FTP
Extracted by mmaFtpRoadmap.sh -i howTos
Follow the steps below.
2) Install dns Binaries.
mmaFtpBinsInstall.sh -i djbdnsFullInstall
3) Specify basic paramters (domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/mmaFtpListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
mmaFtpHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
mmaFtpAdmin.sh -i fullReport
13.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA FTP
Extracted by mmaFtpRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
NOTYET, Pinneke, anything worth mentioning here.
13.2 MMA GNATS
13.2.1 Model and Terminology – MMA GNATS
Extracted by mmaGnatsRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
Objects Overview:
-----------------
mmaGnats Object Processors and Containers:
------------------------------------------
mmaGnatsServerHosts.sh
13.2.2 Files Overview – MMA GNATS
Extracted by mmaGnatsRoadmap.sh -i help
DESCRIPTION
mmaGnats (MailMeAnywhere QMAIL) is a set of consistent
policies built on the QMAIL as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
mmaGnats Commands, each contain a set of related functions
which allow you to accomplish specific tasks. Specifically:
COMMAND TYPE USED BY
mmaGnats.sh action.sh any
mmaGnatsLib.sh library.sh root/any
mmaGnatsBinsPrep.sh action.sh root
mmaGnatsServerHosts.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaGnatsAdmin.sh action.sh root/any
At A Glance
-----------
Basic qmail
-----------
mmaGnats.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaGnatsLib.sh -- To be included in all mmaGnats scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaGnatsBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
mmaGnatsBinsInstall.sh -- Install mmaGnats binaries on opRunHostName
mmaGnatsServerHosts.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
mmaGnatsAdmin.sh -- Start, stop and addNewAccounts
mmaGnatsUserConfig.sh -- Setup Per user environment parameters.
13.2.3 Hints – MMA GNATS
Extracted by mmaGnatsRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A) How Do I setup a null client from scratch?
Follow (A-1), and then:
3) Specify basic null client paramters (smarthost, domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/mmaGnatsListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
mmaGnatsHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
mmaGnatsAdmin.sh -i fullReport
5) Sendout a test message.
mmaGnatsUserConfig.sh -i mailTest
6) Allow users to customize their desired parameters.
mmaGnatsUserConfig.sh
13.2.4 Pointer and References – MMA GNATS
Extracted by mmaGnatsRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
cgi-bin is: /usr/lib/cgi-bin/gnatsweb.pl
Gnats web conf params are in: /etc/gnatsweb/
Web config is in: + /usr/doc/gnatsweb/CUSTOMIZE.vars.gz
13.3 MMA Rsync
13.3.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Rsync
Extracted by mmaRsyncRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
pubCntntSrvr: The server assigned for publishing
a set of mmaRsyncPkgs.
13.3.2 Files Overview – MMA Rsync
Extracted by mmaRsyncRoadmap.sh -i help
At A Glance
-----------
mmaRsync.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaRsyncLib.sh -- To be included in all mmaRsync scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaRsyncPkgs.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
mmaRsyncServers.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
13.3.3 Hints – MMA Rsync
Extracted by mmaRsyncRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A) How Do I setup a xxx scratch?
13.3.4 Pointer and References – MMA Rsync
Extracted by mmaRsyncRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
13.4 MMA Ssh
13.4.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Ssh
Extracted by mmaSshRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
Host Key -- priv/pub key for this host.
Known Hosts -- pub keys of remote hosts
User Key -- priv/pub key of a user at this host
AuthorzedKeys -- pub key of remote users at remote hosts
-- granted access
User Key Export -- Process of exporting the public
-- key of a user to other remote users
13.4.2 Files Overview – MMA Ssh
Extracted by mmaSshRoadmap.sh -i help
mmaSsh (MailMeAnywhere Open SSH) is a set of consistent
policies built on the SSH as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
At A Glance
-----------
Basic SSH
-----------
mmaSsh.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaSshBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for OpenSSH
-- for relevant platforms and versions
-- Install mmaSsh binaries on opRunHostName
mmaSshAdmin.sh -- Start, stop
USAGE
See specific mmaSshXxxx commands.
EXAMPLES
A) How Do I install OpenSSH on my system?
Follow the steps below.
1) Install OpenSSH Binaries.
mmaSshBinsPrep.sh sshFullInstall
B) After the installation, what are the next steps?
1) First, you need to generate the ssh key server
in order to start ssh daemon. Run the following:
mmaSshAdmin.sh -i serverKeyGeneration
This process may take a while.
2) Start running the sshd as root
mmaSshAdmin.sh -i start
3) Generate a key for yourself. The default forUser is
the current user login.
mmaSshAdmin.sh -i userKeyGeneration
or
mmaSshAdmin.sh -p forUser=somename -i userKeyGeneration
4) Try ssh from another machine to the ssh server
that you just install.
FILES
mmaSsh⋆
tehran
Linux
13.4.3 Hints – MMA Ssh
Extracted by mmaSshRoadmap.sh -i howTos
13.4.4 Pointer and References – MMA Ssh
Extracted by mmaSshRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
13.5 MMA Sudo
13.5.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Sudo
Extracted by mmaSudoRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
sudoers file -- list of which users may excute what
-- This file is /etc/sudoers
-- man sudoers for more info
13.5.2 Files Overview – MMA Sudo
Extracted by mmaSudoRoadmap.sh -i help
mmaSudo is a set of consistent
policies built on sudo as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
sudo is able to execute a command as another user.
At A Glance
-----------
Basic Sudo
-----------
mmaSudo.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaSudoBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for sudo
mmaSudoAdmin.sh -- To update the sudoers file
USAGE
See specific mmaSshXxxx commands.
EXAMPLES
A) How Do I install sudo on my system?
Follow the steps below.
1) Install sudo Binaries.
mmaSudoBinsPrep.sh -i fullUpdate
B) After the installation, what are the next steps?
1) Add the user that will allow to run sudo to
the sudoers file with mmaSudoAdmin.sh
FILES
mmaSudo⋆
tehran
Linux
13.5.3 Hints – MMA Sudo
Extracted by mmaSudoRoadmap.sh -i howTos
13.5.4 Pointer and References – MMA Sudo
Extracted by mmaSudoRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
13.6 MMA Tftp
13.6.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Tftp
Extracted by mmaTftpRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
13.6.2 Files Overview – MMA Tftp
Extracted by mmaTftpRoadmap.sh -i help
DESCRIPTION
mmaTftp is a set of consistent facilities
on top of wu-ftp which enforces MMA policies.
Basic DNS Scripts
-----------------
mmaTftp.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaTftpBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for djbFtp
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
-- Install mmaTftp binaries on opRunHostName
mmaTftpHosts.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
mmaTftpAdmin.sh -- Start, stop and addNewAccounts
13.6.3 Hints – MMA Tftp
Extracted by mmaTftpRoadmap.sh -i howTos
Follow the steps below.
2) Install dns Binaries.
mmaTftpBinsInstall.sh -i djbdnsFullInstall
3) Specify basic paramters (domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/mmaTftpListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
mmaTftpHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
mmaTftpAdmin.sh -i fullReport
13.6.4 Pointer and References – MMA Tftp
Extracted by mmaTftpRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
NOTYET, Pinneke, anything worth mentioning here.
Part X
DNS Facilities
13.7 MMA DNS
13.7.1 Model and Terminology – MMA DNS
Extracted by mmaDnsRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
Qualifiers:
-----------
- local: The scope is limited to this host only.
Accomplished using the 127.x.x.x address space.
- net: The scope is limited to this host only.
Accomplished using the network address space
(192.168.x.x, ....)
Server Types:
-------------
- Resolving Server: Runs some form of dnscache.
- Orig Content Server: Runs tinydns and is the origin of data
and provides its data to CopyContentServers.
- Copy Content Server: Runs tinydns and gets its data from
some Orig Content Server.
- Zone Xfer Server: Runs axfrdns and provides zone data.
Copying - Import/Export
-----------------------
We dont use "Primary" or "Secondary" terminology.
We dont use "Master" or "Slave" terminology.
We use Import and Export combined with
net{Orig,Copy}ContentServer
A net{Orig,Copy}ContentServer when exposed to the
outside world can be considered Primary or Secondary.
A localOrigContentServer can be exporting to multiple
netCopyContentServers.
Import and Export Methods are listed below:
Import Methods:
---------------
sshPoll --
--
ZoneXferGet: -- Sets up what it takes to do periodic
-- axfr-get.
Export Methods:
---------------
sshPush --
--
Content Loading:
----------------
mmaDnsEntry{type}{verb} -- Takes domainName and HostName (mma)
mmaDnsEntry{type}{verb} -- Takes domainName and IpAddress
type is one of: {host,alias,mx,childns,...}
verb is one of: {show,update,delete}
Exposed Content Servers
-----------------------
Combinations of netOrig and netCopy contentServers which
have been declared to higher zones (e.g. root servers).
dnsSetup (Valid Values):
------------------------
localResolvingServer -- local cache -- Just available to this host
-- runs dnscache on local 127.x address
netResolvingServer -- external cache -- net
-- runs dnscachex on network IP address
localOrigContentServer -- Orig Content Server -- Local Address
-- runs tinydns on local 127.x address
netOrigContentServer -- Orig Content Server -- Network Address
-- runs tinydns on network 192.168 address
localCopyContentServer -- Copy Content Server -- Local Address
-- runs tinydns on local 127.x address
netCopyContentServer -- Copy Content Server -- Network Address
-- runs tinydns on private 192.168 address
netZoneXferServer: -- Runs axfrdns and provides zone data.
-- Respond to zone transfer requests.
netZoneXferGet: -- Setup axfr-get polls
Permitted Combinations
----------------------
localResolvingServer with
netOrigContentServer
netCopyContentServer
netZoneXferServer
netResolvingServer (privateResolvingServer or publicResolvingServer)
localOrigContentServer
localCopyContentServer
netZoneXferServer
Conflicting Combinations
----------------------
netResolvingServer and (netOrigContentServer or netCopyContentServer)
13.7.2 Files Overview – MMA DNS
Extracted by mmaDnsRoadmap.sh -i help
DESCRIPTION
mmaDns is a set of consistent facilities
on top of DJBDNS which enforces MMA policies.
Basic DNS Scripts
-----------------
mmaDns.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaDnsLib.sh -- To be included in all mmaDns scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaDnsBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for djbDns
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
-- Install mmaDns binaries on opRunHostName
mmaDnsServerHosts.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
mmaDnsAdmin.sh -- Start, stop and addNewAccounts
mmaDnsImports.sh -- Manipulate import zones
opDomainContents.sh -- Fill in the data for orig data servers
--
opDomains.sh -- List of all domains and pointers to the
-- content
opNetNameServices.sh -- /etc/hosts file generator and domain content
-- basic ip address generation.
Basic DNS Items File
--------------------
Related Items Files:
nedaIPAddrxxxxxItems.{priv0,pubC}
opDomainItems.site
Basic Items Files:
mmaDnsServerHostItems.site
mmaDnsCopyItems.site
mmaDnsCopyItems.other
----------
13.7.3 Hints – MMA DNS
Extracted by mmaDnsRoadmap.sh -i howTos
Follow the steps below.
2) Install dns Binaries.
mmaDnsBinsInstall.sh -i djbdnsFullInstall
3) Specify basic paramters (domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/mmaDnsListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
mmaDnsHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
mmaDnsAdmin.sh -i fullReport
13.7.4 Pointer and References – MMA DNS
Extracted by mmaDnsRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Web draws a directed graph for a domain.
http://www.foobar.tm/dns/dnsbajaj.cgi
Life With DJBDns: http://
Part XI
Mail Facilities
Chapter 14
Email Facilities
14.1 Introduction
14.1.1 General Policies & Procedures
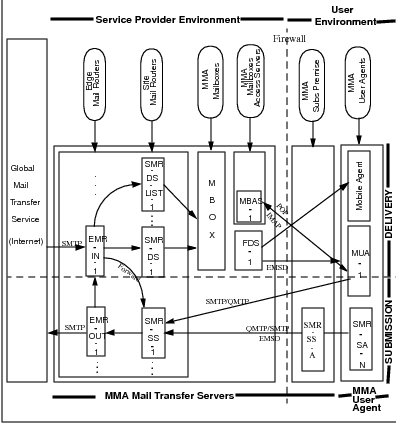
14.1.2 Site Deployment Policies & Procedures
The abbreviations that are used in Figure 14.1
- EMR-IN:
- Edge Mail Router - Inbound
MB provide the description. - EMR-OUT:
- Edge Mail Router - Outbound
MB provide the description. - SMR-DS:
- Site Mail Router - Delivery Server
MB provide the description. - SMR-DS-LIST:
- Site Mail Router - Delivery Server - List
MB provide the description. - SMR-SS:
- Site Mail Router - Submit Server
MB provide the description. - SMR-SA:
- Site Mail Router - Submission Agent
MB provide the description. - MBAS:
- Mail Box Access Server
MB provide the description. - FDS:
- Final Delivery Server
MB provide the description. - MUA:
- Mail User Agent
MB provide the description. - MRUA:
- Mail Retrieval User Agent
MB provide the description. - MSUA:
- Mail Submission User Agent
MB provide the description.
14.2 mmaQmail
14.3 Model and Terminology – MMA Qmail Tools
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
- FQMA: Full Qualified Mail Address -- localPart@domainPart
- localPart: Stuff to the left of @ sign
- domainPart: Domain to the right of @ sign
- qmailAddr: A tupple of (localPart) and qmailCtlFile
- qmailCtlFile: A .qmail or .qmail-xxx file
- qmailAccount: A system account recorded in the users/include
- locDeliveryAcct: same as qmailAccount
- qmailDomainType: One of virDomain or mainDomain
- mbox: A file specification in a qmailCtlFile.
Multiple localPart and qmailAddr may
share the same mbox
- progs: A pipe specification in a qmailCtlFile.
- forwards: A pipe specification in a qmailCtlFile.
Objects Overview:
-----------------
item_qmailHost_{HostName}: Config Parameters for the mail server host.
Server Type is on of:
(submitClientSmtp|submitServerSmtp|fullServer)
Objects below apply to fullServer.
item_qmailDom_{domainName}: Information about a domain.
Both mainDomain and virDomain object types.
Includes pointers back to item_qmailHost and
forward to item_qmailAcctsList.
item_qmailAcctsList_{domainName}: List of item_qmailAcct for domainName
item_qmailAcct: Tupple of
1) systemAcct
2) List of item_qmailAddr
item_qmailAddr:
- addrName (localPart)
- type ((alias|virDom)=tldAddr, person, prog)
- mbox
- forward
- ...
item_distList:
- name
- postingRestrictions
- archiving
- ...
byname/NSP/mailAddr:
- byname mail boxes
mmaQmail Object Processors and Containers:
------------------------------------------
mmaQmailHosts.sh
mmaQmailDoms.sh
mmaQmailAddrs.sh
mmaQmailLists.sh
bynameNspMail.sh
qmailHost Objects:
------------------
qmailHost can be of the types:
submitClientSmtp: Sometimes called "Null Client:
Just submits. Doe not accept smtp
connections.
submitServerSmtp:
fullServer:
14.4 Files Overview – MMA Qmail Tools
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i help
mmaQmailRoadmap.sh
SYNOPSIS
Derived from seedActions.sh, use the -u.
mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -u
DESCRIPTION
mmaQmail (MailMeAnywhere QMAIL) is a set of consistent
policies built on the QMAIL as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
mmaQmail Commands, each contain a set of related functions
which allow you to accomplish specific tasks. Specifically:
COMMAND TYPE USED BY
mmaQmail.sh action.sh any
mmaQmailLib.sh library.sh root/any
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh action.sh root
mmaQmailHosts.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailDoms.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailAddrs.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailAdmin.sh action.sh root/any
mmaQmailInject.sh action.sh any
mmaQmailLists.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh action.sh any
bynameNspMail.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
At A Glance
-----------
Basic qmail
-----------
mmaQmail.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaQmailLib.sh -- To be included in all mmaQmail scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
mmaQmailBinsInstall.sh -- Install mmaQmail binaries on opRunHostName
mmaQmailHosts.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
mmaQmailAdmin.sh -- Start, stop and addNewAccounts
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh -- Setup Per user environment parameters.
mmaQmailAddrs.sh -- mmaQmailAddrItems specify addresses (e.g. postmaster)
-- to be genarted as .qmail- files.
qmailDom
-----------
mmaQmailDoms.sh -- mmaQmailVirDomItems.site specifies visible virtual domains.
-- Verify and ensure creation of accounts
-- for virtual domains (e.g. esro.org and lists.esro.org)
-- add the virtual domains to qmail host configurations.
qmail Mailing Lists
-------------------
mmaQmailLists.sh -- mmaQmailListItems specify information needed to create
-- and activate needed mailing lists.
-- Archiving, web exposure (mhonarc) are all done
-- here.
ByName Support
--------------
bynameNspMail.sh -- Generate and maintain addresses
bynameNspMailList.sh -- Track and control mailing list generation
USAGE
See specific mmaQmailXxxx commands.
EXIT STATUS
opClusterName The cluster name
FILES
mmaQmail⋆
14.5 Hints – Account Management Tools
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A-1) How Do I install Qmail on my system?
Follow the steps below.
0) Setup Open Services Platform Environment.
In /opt/public/osmt/bin/
source opEnvSet.csh -- . opEnvSet.ksh
1) Disable the existing sendmail functionality
mmaSendmailActions.sh -i sendmailDefunct
2) Install Qmail Binaries.
mmaQmailBinsInstall.sh -i qmailFullInstall
A) How Do I setup a null client from scratch?
Follow (A-1), and then:
3) Specify basic null client paramters (smarthost, domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/mmaQmailListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
mmaQmailHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
mmaQmailAdmin.sh -i fullReport
5) Sendout a test message.
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh -i mailTest
6) Allow users to customize their desired parameters.
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh
B: How do I create a new binary kit for a new rev of Linux/SunOs?
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh -i mmaQmailBuildAndInstall
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh -i mmaQmailBinKitMake
C: How Do I Setup an Domain Mail Server?
C: How Do I Setup a mailing list?
14.6 Pointer and References – Account Management Tools
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Life With Qmail: http://
14.7 MMA Qmail
14.7.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Qmail
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
- FQMA: Full Qualified Mail Address -- localPart@domainPart
- localPart: Stuff to the left of @ sign
- domainPart: Domain to the right of @ sign
- qmailAddr: A tupple of (localPart) and qmailCtlFile
- qmailCtlFile: A .qmail or .qmail-xxx file
- qmailAccount: A system account recorded in the users/include
- locDeliveryAcct: same as qmailAccount
- qmailDomainType: One of virDomain or mainDomain
- mbox: A file specification in a qmailCtlFile.
Multiple localPart and qmailAddr may
share the same mbox
- progs: A pipe specification in a qmailCtlFile.
- forwards: A pipe specification in a qmailCtlFile.
Objects Overview:
-----------------
item_qmailHost_{HostName}: Config Parameters for the mail server host.
Server Type is on of:
(submitClientSmtp|submitServerSmtp|fullServer)
Objects below apply to fullServer.
item_qmailDom_{domainName}: Information about a domain.
Both mainDomain and virDomain object types.
Includes pointers back to item_qmailHost and
forward to item_qmailAcctsList.
item_qmailAcctsList_{domainName}: List of item_qmailAcct for domainName
item_qmailAcct: Tupple of
1) systemAcct
2) List of item_qmailAddr
item_qmailAddr:
- addrName (localPart)
- type ((alias|virDom)=tldAddr, person, prog)
- mbox
- forward
- ...
item_distList:
- name
- postingRestrictions
- archiving
- ...
byname/NSP/mailAddr:
- byname mail boxes
mmaQmail Object Processors and Containers:
------------------------------------------
mmaQmailHosts.sh
mmaQmailDoms.sh
mmaQmailAddrs.sh
mmaQmailLists.sh
bynameNspMail.sh
qmailHost Objects:
------------------
qmailHost can be of the types:
submitClientSmtp: Sometimes called "Null Client:
Just submits. Doe not accept smtp
connections.
submitServerSmtp:
fullServer:
14.7.2 Files Overview – MMA Qmail
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i help
mmaQmailRoadmap.sh
SYNOPSIS
Derived from seedActions.sh, use the -u.
mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -u
DESCRIPTION
mmaQmail (MailMeAnywhere QMAIL) is a set of consistent
policies built on the QMAIL as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
mmaQmail Commands, each contain a set of related functions
which allow you to accomplish specific tasks. Specifically:
COMMAND TYPE USED BY
mmaQmail.sh action.sh any
mmaQmailLib.sh library.sh root/any
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh action.sh root
mmaQmailHosts.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailDoms.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailAddrs.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailAdmin.sh action.sh root/any
mmaQmailInject.sh action.sh any
mmaQmailLists.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh action.sh any
bynameNspMail.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
At A Glance
-----------
Basic qmail
-----------
mmaQmail.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaQmailLib.sh -- To be included in all mmaQmail scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
mmaQmailBinsInstall.sh -- Install mmaQmail binaries on opRunHostName
mmaQmailHosts.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
mmaQmailAdmin.sh -- Start, stop and addNewAccounts
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh -- Setup Per user environment parameters.
mmaQmailAddrs.sh -- mmaQmailAddrItems specify addresses (e.g. postmaster)
-- to be genarted as .qmail- files.
qmailDom
-----------
mmaQmailDoms.sh -- mmaQmailVirDomItems.site specifies visible virtual domains.
-- Verify and ensure creation of accounts
-- for virtual domains (e.g. esro.org and lists.esro.org)
-- add the virtual domains to qmail host configurations.
qmail Mailing Lists
-------------------
mmaQmailLists.sh -- mmaQmailListItems specify information needed to create
-- and activate needed mailing lists.
-- Archiving, web exposure (mhonarc) are all done
-- here.
ByName Support
--------------
bynameNspMail.sh -- Generate and maintain addresses
bynameNspMailList.sh -- Track and control mailing list generation
USAGE
See specific mmaQmailXxxx commands.
EXIT STATUS
opClusterName The cluster name
FILES
mmaQmail⋆
14.7.3 Hints – MMA Qmail
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A-1) How Do I install Qmail on my system?
Follow the steps below.
0) Setup Open Services Platform Environment.
In /opt/public/osmt/bin/
source opEnvSet.csh -- . opEnvSet.ksh
1) Disable the existing sendmail functionality
mmaSendmailActions.sh -i sendmailDefunct
2) Install Qmail Binaries.
mmaQmailBinsInstall.sh -i qmailFullInstall
A) How Do I setup a null client from scratch?
Follow (A-1), and then:
3) Specify basic null client paramters (smarthost, domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/mmaQmailListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
mmaQmailHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
mmaQmailAdmin.sh -i fullReport
5) Sendout a test message.
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh -i mailTest
6) Allow users to customize their desired parameters.
mmaQmailUserConfig.sh
B: How do I create a new binary kit for a new rev of Linux/SunOs?
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh -i mmaQmailBuildAndInstall
mmaQmailBinsPrep.sh -i mmaQmailBinKitMake
C: How Do I Setup an Domain Mail Server?
C: How Do I Setup a mailing list?
14.7.4 Pointer and References – MMA Qmail
Extracted by mmaQmailRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Life With Qmail: http://
14.8 MMA IMAP
14.8.1 Model and Terminology – MMA IMAP
Extracted by mmaImapRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
Objects Overview:
-----------------
mmaGnats Object Processors and Containers:
------------------------------------------
mmaGnatsServerHosts.sh
14.8.2 Files Overview – MMA IMAP
Extracted by mmaImapRoadmap.sh -i help
DESCRIPTION
mmaGnats (MailMeAnywhere QMAIL) is a set of consistent
policies built on the QMAIL as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
mmaGnats Commands, each contain a set of related functions
which allow you to accomplish specific tasks. Specifically:
COMMAND TYPE USED BY
mmaGnats.sh action.sh any
mmaGnatsLib.sh library.sh root/any
mmaGnatsBinsPrep.sh action.sh root
mmaGnatsServerHosts.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaGnatsAdmin.sh action.sh root/any
At A Glance
-----------
Basic qmail
-----------
mmaGnats.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaGnatsLib.sh -- To be included in all mmaGnats scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaGnatsBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
mmaGnatsBinsInstall.sh -- Install mmaGnats binaries on opRunHostName
mmaGnatsServerHosts.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
mmaGnatsAdmin.sh -- Start, stop and addNewAccounts
mmaGnatsUserConfig.sh -- Setup Per user environment parameters.
14.8.3 Hints – MMA IMAP
Extracted by mmaImapRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A) How Do I setup a null client from scratch?
Follow (A-1), and then:
3) Specify basic null client paramters (smarthost, domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/mmaGnatsListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
mmaGnatsHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
mmaGnatsAdmin.sh -i fullReport
5) Sendout a test message.
mmaGnatsUserConfig.sh -i mailTest
6) Allow users to customize their desired parameters.
mmaGnatsUserConfig.sh
14.8.4 Pointer and References – MMA IMAP
Extracted by mmaImapRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
cgi-bin is: /usr/lib/cgi-bin/gnatsweb.pl
Gnats web conf params are in: /etc/gnatsweb/
Web config is in: + /usr/doc/gnatsweb/CUSTOMIZE.vars.gz
Part XII
Web Facilities
Chapter 15
Web Server Tools
15.1 opWebServers
15.2 MMA Web
15.2.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Web
Extracted by mmaWebRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
Objects Overview:
-----------------
item_webSrv_{HostName}: Config Parameters for the Web server host.
This config params include:
- reference: pointer to the item_webDom
for domain's information. These
domains are the one hosted by this hostname.
- serverType: could be one of
fullServer, ...
item_webDom_{domainName}: Information about a domain.
- domainName
- serverReference
- doc basedir location
mmaWeb Object Processors and Containers:
------------------------------------------
mmaWebServers.sh
mmaWebDomains.sh
mmaWebAdmin.sh
bynameNspWebServers.sh
15.2.2 Files Overview – MMA Web
Extracted by mmaWebRoadmap.sh -i help
mmaWebRoadmap.sh
SYNOPSIS
Derived from seedActions.sh, use the -u.
mmaWebRoadmap.sh -u
DESCRIPTION
mmaWeb is a set of consistent policies built on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
mmaWeb Commands, each contain a set of related functions
which allow you to accomplish specific tasks. Specifically:
COMMAND TYPE USED BY
mmaWebLib.sh library any
mmaWebServers.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaWebDomains.sh subjectAction.sh root/any
mmaWebAdmin.sh action.sh root/any
bynameNspWebServers.sh action.sh root/any
At A Glance
-----------
Basic web
-----------
mmaWebLib.sh -- To be used by mmaWebXXX family
mmaWebServers.sh -- Configure a system for web server.
- For subject host, create apache
conf file and update dns stuff
mmaWebDomains.sh -- Configure web domain
- For subject domain, append the
virtual domain info to apache
conf file and update dns stuff.
mmaWebAdmin.sh -- Web server and domains maintenance.
ByName Support
--------------
bynameNspWebServers.sh -- Generate Web feature for byname subscriber.
USAGE
See specific mmaWebXxxx commands.
FILES
mmaWeb⋆
15.2.3 Hints – MMA Web
IMAP
Extracted by mmaWebRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A) How do I install new web server on my system?
Follow the steps below.
1) Make sure that the system has its input
item in the mmaWebServerItems.site:
item_webSrv_{hostName}
domainRefList is a list of domains to be
hosted by the system and it correspond
to each item in mmaWebDomainItems.site itemsFile.
2) ....
IMAP
15.2.4 Pointer and References – MMA Web
Extracted by mmaWebRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Apache: http://www.apache.org
Part XIII
Database and Directory Facilities
Chapter 16
Name Services
16.1 nedaIPaddr.sh
16.2 opNetNameServices
Chapter 17
Directory Services Tools
Directory services is a set of tool that provides.....
17.1 Model and Terminology – Directory Services Tools
17.2 Files Overview – Directory Services Tools
17.3 Hints – Directory Services Tools
17.4 Pointer and References – Directory Services Tools
Chapter 18
Data Base Facilities
pgsql and mysql go here.
Part XIV
Security Facilties
Chapter 19
Key Management – Remote Access
lcaPgp Comes Here.
Chapter 20
Security Tools
20.1 opSecurity
opSecurity can be used as ....
Part XV
Development and Analysis Tools
Chapter 21
Development Facilities
21.1 CVS
Chapter 22
Software Management Tools
22.1 opSwPkgs
Chapter 23
Performance and Monitoring Tools
lcaNagios goes here.
Part XVI
Libre Content Production and Publication
Chapter 24
LaTeX
Chapter 25
Libre Content Processing
25.1 MMA Published Content
25.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Published Content
Extracted by mmaCntntRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
pkgCombContainer - the items file container of the
combined pkgs.
pkgFamily - the family name that the pkg belong to.
Objects Overview:
-----------------
mmaCntntPkgItems.{pkgFamily} - Items file for each family.
Each pkg belongs to a family.
Families are kept in separate items files.
item_cntntPkg_{pkgName} - Information for each package.
Each pkg reference points to
item_access_{pkgName} which reside within
the same file.
item_access_{pkgName} - Complete access info for a pkg.
Content type could be one of:
sw,doc,svc.
Each cntnt is restricted to one of:
free,dist(distribution),conf(confidential)
mmaCntntPkgCombItems.{category} - Each combined package belongs to a
category. The category is one of:
proj,usage,platform. The category may
increase over time.
item_cntntPkgComb_{pkgCombName} - Contain info for combined pkg.
This include pointer to mmaCntntPkgItems.{pkgFamily}
and pkg ref.
item_cntntPubSrvr_{hostName} - Each host will published certain
pkgs (combined or individual) according to
this item.
A pkg can be one of these type:
- "sw"
- "svc"
- "doc"
These then map onto http and ftp dirs based on the following
hierarchy.
- ftp/http Roots
- doc.dist (For Distribution)
- doc.conf (Confidential)
- doc.free (Unrestricted)
- sw.free
- svc.free
- origin (e.g. neda)
- family (e.g. leap)
- pkgName (esro)
- moduleName (mulPub)
- revision
- accessPage (Generated)
- categories
- projs
- owners
- usage
- accessPagesList
(Any Combination Pointing to accessPage)
mmaCntnt Object Processors and Containers:
------------------------------------------
mmaCntntPkgs.sh
mmaCntntPkgCombs.sh
mmaCntntPubServers.sh
25.1.2 Files Overview – MMA Published Content
Extracted by mmaCntntRoadmap.sh -i help
At A Glance
-----------
Basic cntnt
-----------
mmaCntntRoadmap.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
mmaCntntLib.sh -- To be included in all mmaPubCntnt scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
mmaCntntPkgs.sh -- Prepare each pkg for web and ftp transfer.
This includes copying source or docs
to the correct directory as well as
creating access page in html format
for each package.
mmaCntntPubServers.sh -- Prepare each host to become the
published content server.
25.1.3 Hints – MMA Published Content
Extracted by mmaCntntRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A) How Do I setup a public content server from scratch?
25.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA Published Content
Extracted by mmaCntntRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
NOTYET
25.2 lcnLcnt
Chapter 26
Image Processing
Sections related to sane go here.
Chapter 27
Video Processing
publication. camcorder.
Chapter 28
Account Management Tools
28.1 Model and Terminology – Account Management Tools
Extracted by opAcctRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
ITEM FILES
----------
28.2 Files Overview – Account Management Tools
Extracted by opAcctRoadmap.sh -i help
28.3 Hints – Account Management Tools
Extracted by opAcctRoadmap.sh -i howTos
28.4 Pointer and References – Account Management Tools
Extracted by opAcctRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Mma man pages.
Chapter 29
Cron and At Tools
29.1 Model and Terminology – Cron and At Tools
Extracted by opCronRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
- cronEntry:
- cronTable:
Objects Overview:
-----------------
29.2 Files Overview – Cron and At Tools
opAcctRoadmap-help.tex
Extracted by opCronRoadmap.sh -i help
DESCRIPTION
opCron (MailMeAnywhere CRON) is a set of consistent
policies built on the CRON as a CAPABILITY and on
(OSMT) Open Services Management Tools.
opCron Commands, each contain a set of related functions
which allow you to accomplish specific tasks. Specifically:
COMMAND TYPE USED BY
opCron.sh action.sh any
opCronLib.sh library.sh root/any
opCronActions.sh action.sh root/any
At A Glance
-----------
Basic qmail
-----------
opCron.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
opCronLib.sh -- To be included in all opCron scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
opCronActions.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
opAcctRoadmap-help.tex
29.3 Hints – Cron and At Tools
Extracted by opCronRoadmap.sh -i howTos
A-1) How Do I install Qmail on my system?
Follow the steps below.
0) Setup Open Services Platform Environment.
In /opt/public/osmt/bin/
source opEnvSet.csh -- . opEnvSet.ksh
1) Disable the existing sendmail functionality
mmaSendmailActions.sh -i sendmailDefunct
2) Install Qmail Binaries.
opCronBinsInstall.sh -i qmailFullInstall
A) How Do I setup a null client from scratch?
Follow (A-1), and then:
3) Specify basic null client paramters (smarthost, domain, ...)
In ../siteControl/nedaPlus/opCronListItems.main
add an entry for your host. Then:
opCronHosts.sh -s tehran -a configure
4) Verify and Monitor installation
opCronAdmin.sh -i fullReport
5) Sendout a test message.
opCronUserConfig.sh -i mailTest
6) Allow users to customize their desired parameters.
opCronUserConfig.sh
B: How do I create a new binary kit for a new rev of Linux/SunOs?
opCronBinsPrep.sh -i opCronBuildAndInstall
opCronBinsPrep.sh -i opCronBinKitMake
C: How Do I Setup an Domain Mail Server?
C: How Do I Setup a mailing list?
29.4 Pointer and References – Cron and At Tools
Extracted by opCronRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Cron man pages.
Chapter 30
sudo
Part XVII
Common Components – Service and User Environment
Part XVIII
Service Libre Components
Chapter 31
Printers Management Tools
31.1 opPrHosts
31.2 nedaPrint
nedaPrint is used to ....
Chapter 32
Voice Over IP (VoIP)
lcaVoipRoadmap goes here.
Chapter 33
Assigned Names and Numbers
33.1 Password File Accounts
| Category | UID Range | GID Range | Naming Convention | Home Directory | Shell |
| System Acct | 0 - 99 | see Section... | /acct/sys | ksh | |
| Employee | 100 - 4999 | see Section... | /acct/employee | ksh | |
| Contractor | 5000 - 9999 | see Section... | /acct/contractor | ksh | |
| Alumni | 10000 - 14999 | see Section... | /acct/alumni | ksh | |
| Associate | 15000 - 15999 | see Section... | /acct/associate | ksh | |
| Reserved | 16000 - 19999 | ||||
| Subscriber | 20000 - 34999 | see Section... | /acct/subs | ksh | |
| User | 35000 - 49999 | see Section... | /acct/user | ksh | |
| Program Acct | 50000 - 54999 | see Section... | ksh | ||
33.1.1 Employee Account
33.1.2 Contractor Account
33.1.3 Alumni Account
33.1.4 Associate Account
33.1.5 System Program Accounts
| User Name (Alias) | User ID | Group Name | Group ID |
| alias | 50001 | nofiles | 50001 |
| qmaild | 50002 | nofiles | 50001 |
| qmaill | 50003 | nofiles | 50001 |
| qmailp | 50004 | nofiles | 50001 |
33.1.6 System Program Groups
| User Name (Alias) | User ID | Group Name | Group ID |
| qmailq | 50005 | qmail | 50002 |
| qmailr | 50006 | qmail | 50002 |
| qmails | 50007 | qmail | 50002 |
33.1.7 Subscribers (Authenticated)
Subscriber Group ID is 50004
| User Name (Alias) | User ID | Group Name | Description | |
| Qmail | sa-00001 – sa-00003 | 15001 - 15003 | subscrbr | Reserved |
| sa-00004 | 15004 | subscrbr | Subscriber 1.lastName.firstName | |
| ....... | ||||
| EZMLM | ||||
| EMSD | ||||
33.1.8 QMail Virtual Domain
| User Name (Alias) | User ID | Group Name | Group ID | Description | |
| Qmail | qvd-0001 | 11001 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom freeprotocols.org |
| qvd-0002 | 11002 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom byname.net | |
| qvd-0003 | 11003 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom byname.com | |
| qvd-0004 | 11004 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom bynumber.net | |
| qvd-0005 | 11005 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom bynumber.com | |
| qvd-0006 | 11006 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom emsd.org | |
| qvd-0007 | 11007 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom esro.org | |
| qvd-0008 | 11008 | virqmdom | 50003 | QmailVirDom leapforum.org | |
Chapter 34
System Management and Configuration
34.1 Introduction
Below is the general road map to use OSMT tools for creating system environment.
INITIAL SETUP
=============
- Operating System -+
- Installation | opGenesis.sh
- Patching }---- opSolAdmin.sh
- Reproduction | opLinuxAdmin.sh
- ... -+
- Profile & Identity -+
- Name assignment }--- opSysIdentities
- ... -+
- Account Generation -+
- Genesis |
- employee, contractor, ... }--- opAcctUsers.sh
- subscriber |
- ... -+
- Disk Configuration & Access -+ opDiskDrives.sh
- mount disk |--- opDiskSegments.sh
- Backup and Replication |
- ... -+
GENERAL FEATURES
================
- Mail Configuration -+
- Qmail | mmaQmail.⋆
- IMAP }--- mmaImap.⋆
- LEAP |
- ... -+
- Printer Configuration }--- opPrHosts.sh
- Web Configuration }--- opWebServers.sh
- Software }--- opSwPkgs.sh
- Name Servers
- DNS
- Hosts
- ...
- FTP Servers
- Directory Services
- Security
BYNAME FEATURES
===============
- Mail Account -+
|
- LEAP |
}-- bynameNsp⋆
- Web Page |
|
- Subscriber -+
34.2 opSysMgmtActions
This tool is used to ....
34.3 nedaSysMgmtActions
This tools is used specificcally for nedaPlus cluster...
34.4 dotIntra Cluster
Part XIX
User Environment Components
Chapter 35
ByStar Libre Emacs Office Environment (BLEOE)
Chapter 36
Wlan Facilities
Chapter 37
Browser Facilities
Part XX
Native Libre Components
Chapter 38
VoRDE
38.1 MMA VoRDE
38.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA VoRDE
Extracted by mmaVordeRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
38.1.2 Files Overview – MMA VoRDE
Extracted by mmaVordeRoadmap.sh -i help
38.1.3 Hints – MMA VoRDE
Extracted by mmaVordeRoadmap.sh -i howTos
C: How Do I Setup a mailing list?
38.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA VoRDE
Extracted by mmaVordeRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Mma man pages.
Chapter 39
LEAP
39.1 MMA EMSD
39.1.1 Model and Terminology – MMA EMSD
Extracted by mmaEmsdRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Terminology and Model:
======================
39.1.2 Files Overview – MMA EMSD
Extracted by mmaEmsdRoadmap.sh -i help
39.1.3 Hints – MMA EMSD
Extracted by mmaEmsdRoadmap.sh -i howTos
C: How Do I Setup a mailing list?
39.1.4 Pointer and References – MMA EMSD
Extracted by mmaEmsdRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
Mma man pages.
Part XXI
Obsoleted or Deprecated Components
39.2 MMA Jetspeed
39.2.1 Model and Terminology – MMA Jetspeed
Extracted by bynameJetspeedRoadmap.sh -i modelAndTerminology
Part 3 of FIAS document also includes
relevant documentation.
New Documentation should be added here.
Terminology and Model:
======================
Objects Overview:
-----------------
Templates:
----------
See Part 3 of FIAS.
State Table:
------------
See part 3 of FIAS.
39.2.2 Files Overview – MMA Jetspeed
Extracted by bynameJetspeedRoadmap.sh -i help
At A Glance
===========
bynameJetspeedRoadmap.sh -- This File. General Orientation and Information
bynameJetspeedLib.sh -- To be included in all bynameJetspeed scripts.
General configuration parameters and
general useful functions go here
bynameJetspeedBinsPrep.sh -- Prepare binary files for qmail/ezmlm
-- for relevant pltforms and versions
bynameJetspeedServers.sh -- For subject host, configure qmail
bynameJetspeedAdmin.sh -- Start, stop, Review Logs
Interfaces To Byname Module
===========================
bynameJetspeedActions.sh -- Called from Java code
Sychronization scripts? Where are they?
39.2.3 Hints – MMA Jetspeed
Extracted by bynameJetspeedRoadmap.sh -i howTos
-) How Do I rebuild the ⋆whole⋆ byname system from sources?
There are three steps invoved.
1) Obtaining The Sources
See: How Do I obtain the sources?
2) Building The Package
See: How Do I Build the ByName Package?
3) Installing the Component And Activating The Server
See: How Do I install the ByName component?
See: How Do I administer the ByName component?
-) How Do I obtain the sources?
The build procedure expects that you are working in
/sandbox/mine/pinneke
You should also have access to the global CVSROOT.
cd /sandbox/mine/pinneke; /usr/devenv/mapFiles/byname/web/jetspeed/current.sh
If you are doing development on the production side,
cd /l1/sandbox/mine/pinneke; /usr/devenv/mapFiles/byname/web/jetspeed/current.sh
-) How Do I Build the ByName Package?
From the Intra environment, obtain, all the byname needed content.
cd /sandbox/mine/pinneke; bynameJetspeedBinsPrep.sh -v -n showRun -s relCandidate -a zzzz
Make sure that you are on the right machine/side where you
want the package to be built. Then,
bynameJetspeedBinsPrep.sh -v -n showRun -s relCandidate -a srcBuildAndPkg
-) How Do I install the ByName component?
bynameJetspeedServers.sh -v -n showRun -s tehran -a compUpdate
-) How Do I administer the ByName component?
bynameJetspeedAdmin.sh
-) Once a full build is in place how do I do quick cycle development?
o- bynameJetspeedBinsPrep.sh -v -n showRun -s relCandidate -a srcBuild
o- bynameJetspeedServers.sh -v -n showRun -s tehran -a jetspeedUpdate
o- bynameJetspeedServers.sh -v -n showRun -s tehran -a serviceRestart
-) How to customize between byname.com and byname.net
content?
In order to be able to customize the content of
the web page, velocity is used to embed dynamic content
in web sites. User guide is available at:
http://jakarta.apache.org/velocity/user-guide.html.
You need to create a file named bynameConfigFile.vm.bynametmpl
in /sandbox/mine/pinneke/byname-jetspeed/webapp/WEB-INF/templates/vm
This config file will have the following variable:
#set( = "<!var:domainName>" )
This file will be included inside the content that
need to be customize for the .com or .net
For example: the logo for byname.com and byname.net
has to be different depending on the domain.
The file that are responsible for this action is in
/sandbox/mine/pinneke/byname-jetspeed/webapp/WEB-INF/templates/vm/layouts/html/default.vm
Inside this file, put the following:
#parse( "bynameConfigFile.vm" )
.....
.....
..... (any HTML tag)
#if ( "" == "byname.com.intra" || "" == "byname.com" )
<TD><IMG SRC=".setURI("byname/images/comlogo.gif").Absolute" /></TD>
#elseif ( "" == "byname.net.intra" || "" == "byname.net" )
<TD><IMG SRC=".setURI("byname/images/netlogo.gif").Absolute" /></TD>
#end
After you edit this file, do quick cycle.
(See: Once a full build is in place how do I do quick cycle development?)
The bynameJetspeedBinsPrep.sh will call the bynameJetspeedServers.sh to
update jetspeed. When bynameJetspeedServers.sh is called, it looks for all
the files that end with .bynametmpl and doing global replacement
for <!var:xxxx> with wahtever specified in the bynameJetspeedServers.sh.
39.2.4 Pointer and References – MMA Jetspeed
Extracted by bynameJetspeedRoadmap.sh -i pointersAndReferences
http://jakarta.apache.org/